Cleaning Cooling Lubricants – Treating Coolant
There are many names for cooling lubricants. Coolant and metalworking fluid are frequently used terms. In everyday language, terms like cutting oil or cutting fluid are also used.
Meaning of Cooling Lubricants
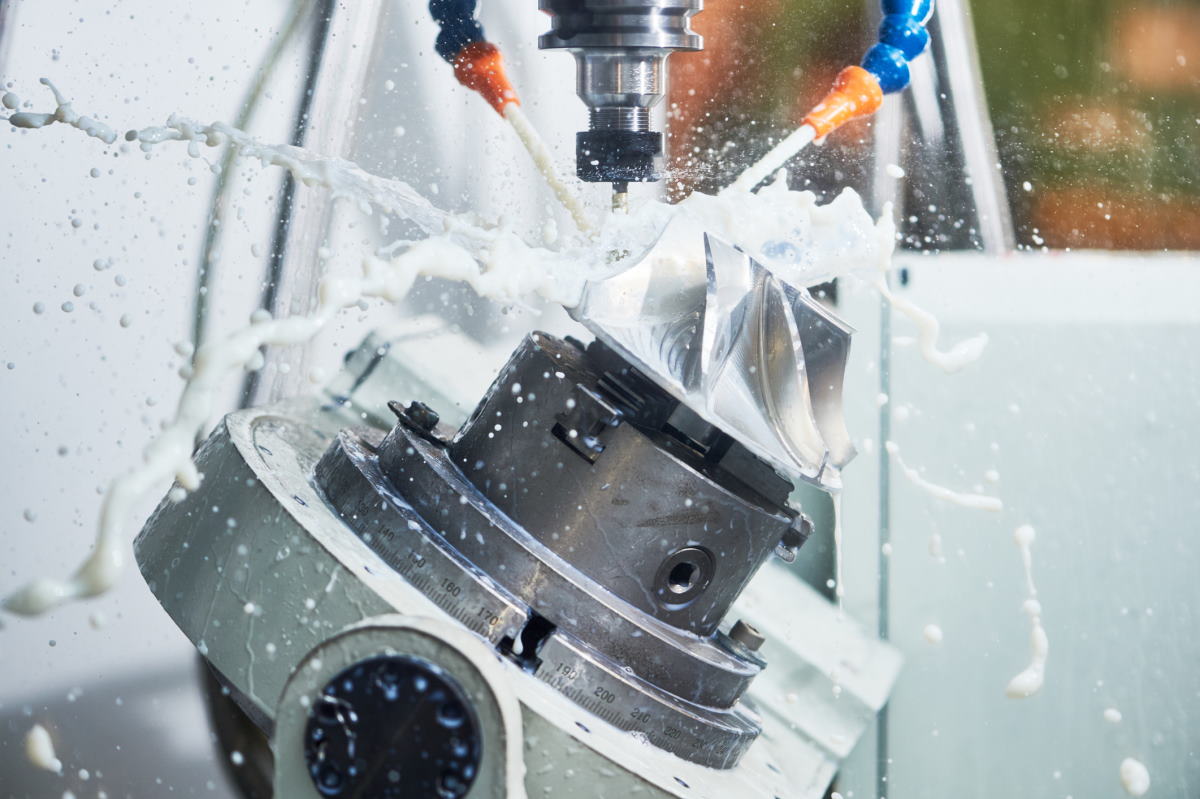

Many industrial manufacturing companies rely on cooling lubricants because they serve to dissipate heat generated by friction between the tool and the workpiece, as well as to lubricate the machining processes.
It is inherent in the nature of metalworking that contaminants quickly accumulate in the coolant. Oils, particles from grinding wheels, workpieces, and tools contaminate the cooling lubricant and can negatively affect work results.
Coolant treatment in the metalworking industry
In the following article, you will learn what points should be considered and the importance of coolant treatment in the metalworking industry. If you would like professional advice, please contact us — we are happy to assist you. Otherwise, enjoy reading.
Contents:
- Problems with Contaminated Coolant
- Coolant Treatment and Maintenance
- Removing Floating Contaminants
- Costs Incurred in Cleaning Cooling Lubricants
- Maintenance and Compliance with Safety Measures When Handling Coolant
- New Procurement of Coolant Despite Treatment
- Conclusion on Coolant Maintenance and Treatment
Problems with Contaminated Coolant
Contaminants such as metal chips and particles, which inevitably arise during the machining of workpieces, enter the cooling lubricant. If these contaminants are not removed from the coolant system, damage and defects to workpieces, tools, and other system components are unavoidable. For this reason, continuous cleaning of the lubricants is of utmost importance to ensure smooth manufacturing operations.
Health aspects also play a role. Improperly treated and contaminated cooling lubricants tend to develop mold and bacterial infestations. This poses significant health risks to machine operators.
Learn more here:
https://www.osha.gov/metalworking-fluids/manual
https://www.osha.gov/metalworking-fluids/health-effects
Chip Removal
Large chips produced during machining can be most easily removed by chip extraction. The chips settle to the bottom of the coolant tank and are then removed using a conveyor belt or chip conveyor. This is a very simple way to remove large amounts of contaminants from the coolant.
Filtration
To remove smaller particles from the coolant that cannot be extracted by a chip conveyor, a filtration system must be used.
Different Filtration Systems Are Used Depending on the Application
Belt filters are frequently used because they can operate continuously and the filter medium does not need to be changed manually as often—the used filter belt simply rolls forward. The dirty filter belt collects in a container and is disposed of at regular intervals.
Other types of filtration are also used with cooling lubricants, such as the classic bag filter. These often serve as supplementary fine filtration to remove smaller particles that the belt filter system cannot capture.
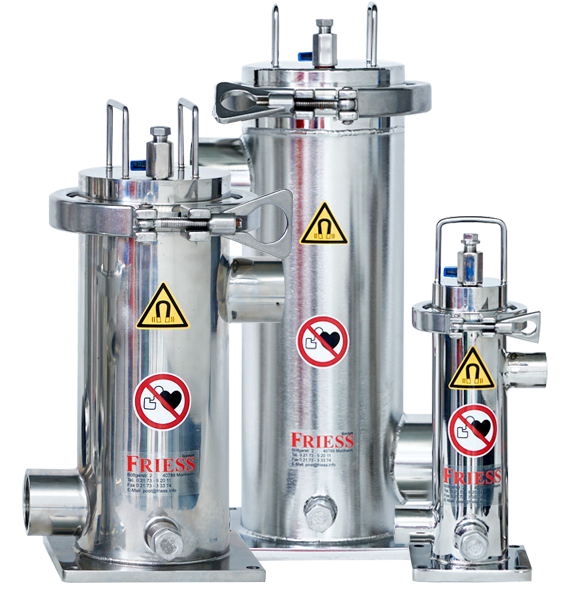
A special case is the magnetic filter, which can only remove magnetic particles like steel or stainless steel from the coolant but does so very effectively. This often eliminates the need for a band filter or other additional filtration.
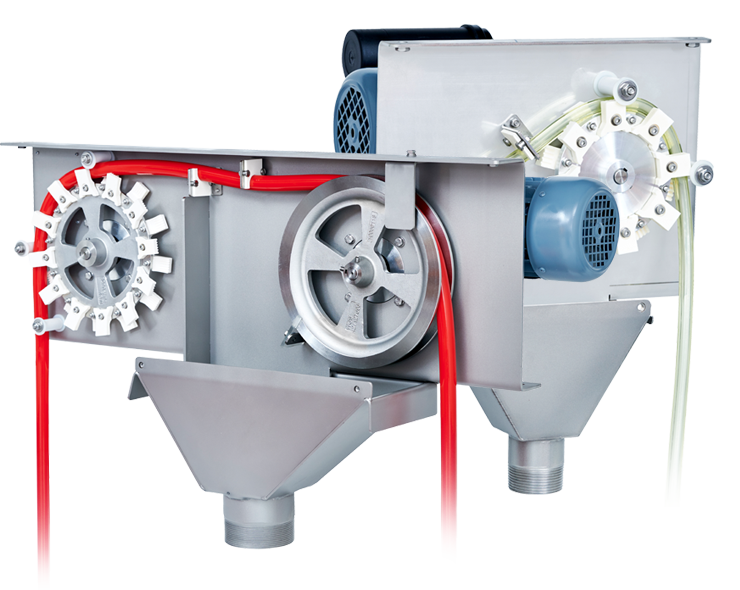
Removing Floating Contaminants
An oil skimmer can be used to skim off floating contaminants. These are usually oils such as grinding oil or hydraulic oil, but also other oily light liquids.
Oil skimmers come in different designs. For smaller tanks, belt skimmers are often used. For larger tanks or sumps, the tube skimmer is the preferred choice.
Maintenance and Compliance with Safety Measures When Handling Coolant
Every operating system must be operated and maintained. The required personnel effort increases the overall costs. However, in a well-functioning coolant system, the personnel required for maintenance and monitoring is very low. Improper use of coolants can pose health risks. Therefore, various rules must be observed or implemented as preventive measures.
Learn more about occupational safety compliance when using coolants:
Metalworking Fluids: Safety and Health Best Practices Manual
https://www.osha.gov/metalworking-fluids/manual
What Costs Are Incurred in Cleaning Cooling Lubricants and Where Can Savings Be Made?
Coolant maintenance often requires several processing steps and stations before the cooling lubricants are ready for use again. Besides the purchase of technical equipment such as magnetic filters, oil skimmers, chip conveyors, and possibly others, the operating costs break down as follows:
Filter Consumables
Filter consumables for treating coolants can include filter media, but also tubes for tube skimmers or belts for belt skimmers.
Cleaning systems like centrifuges do not require consumables but have high energy consumption.
Only the magnetic filter operates without consumables or energy and is also not subject to wear.
Savings
Maintaining the cooling lubricant leads to savings in various cost areas that offset the expenses for maintenance:
- Reduced wear on pumps, valves, nozzles, and tools
- Decreased downtime due to less wear and less frequent coolant changes
- Lower costs for coolant concentrate due to extended service life
Buying Additional Coolant
Even with the best maintenance, it is unavoidable that coolants need to be replenished. This can happen due to leaks or necessary adjustments in concentration. The service life of coolant cannot be extended indefinitely and will eventually require replacement.
BUT:
Through cleaning and treatment of coolant, the overall coolant consumption is significantly lower than without cleaning. Additionally, the reduced amounts of coolant do not have to be disposed of at high cost or treated in wastewater facilities.
Conclusion on Coolant Maintenance and Treatment
Cleaning and treating cooling lubricants is an essential part of every coolant system. Filtration and treatment require investment in treatment equipment. However, treatment generally offers economic advantages due to significantly reduced coolant consumption and lower overall effort related to the coolant. This results in lower expenses for purchasing coolant as well as reduced disposal costs due to the decreased amount of used coolant.
The environmental aspect should not be overlooked: the less coolant is needed, the less oil is purchased and disposed of. This reduces the ecological footprint of manufacturing and saves CO₂—a factor that is becoming increasingly important for manufacturing companies.
If you have questions about treating your cooling lubricants, we are happy to assist you by phone during business hours.
Do you want to know how to best test the condition of your coolant? Here you can find all important parameters and their corresponding measurement methods: Check your coolant!
Overview of the advantages of coolant reconditioning:
- Low expenses for purchasing coolant
- Significantly reduced coolant consumption
- No consumables required for FRIESS systems
- Lower disposal costs due to reduced amounts of used coolant
- Reduced downtime due to fewer changes and damages

Many manufacturing companies rely on coolant in their manufacturing processes. These coolants decrease the heat generated by friction in machining processes and also ...

Application: Machining of large stainless steel parts for marine and pump apllications.

A manufacturer of automotive components uses different grinding machines in order to grind parts for steering systems.
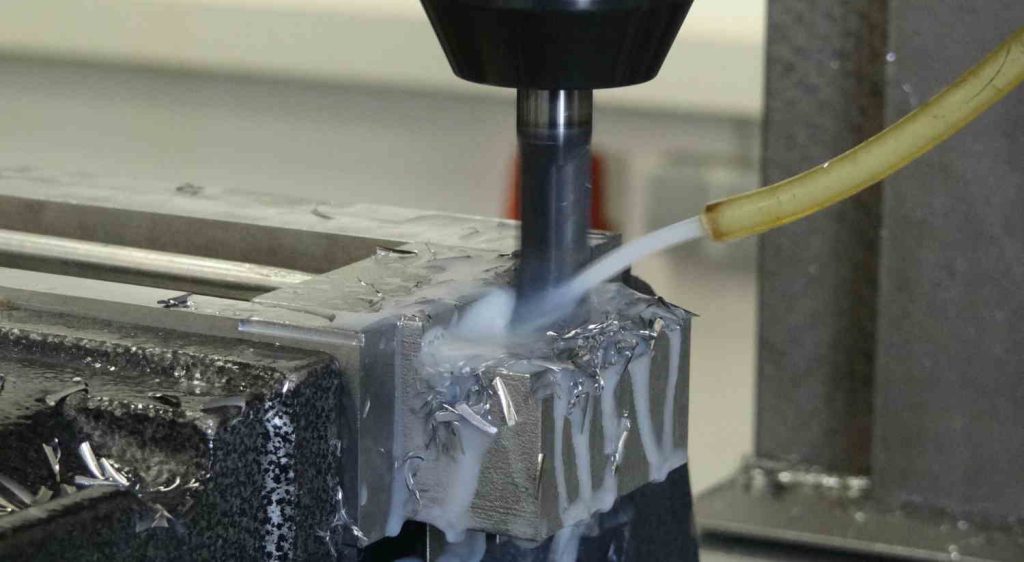

Learn about the regulations and methods that must be followed when handling cooling lubricants.